PPT Intro to the Microscope PowerPoint Presentation, free download ID4240856
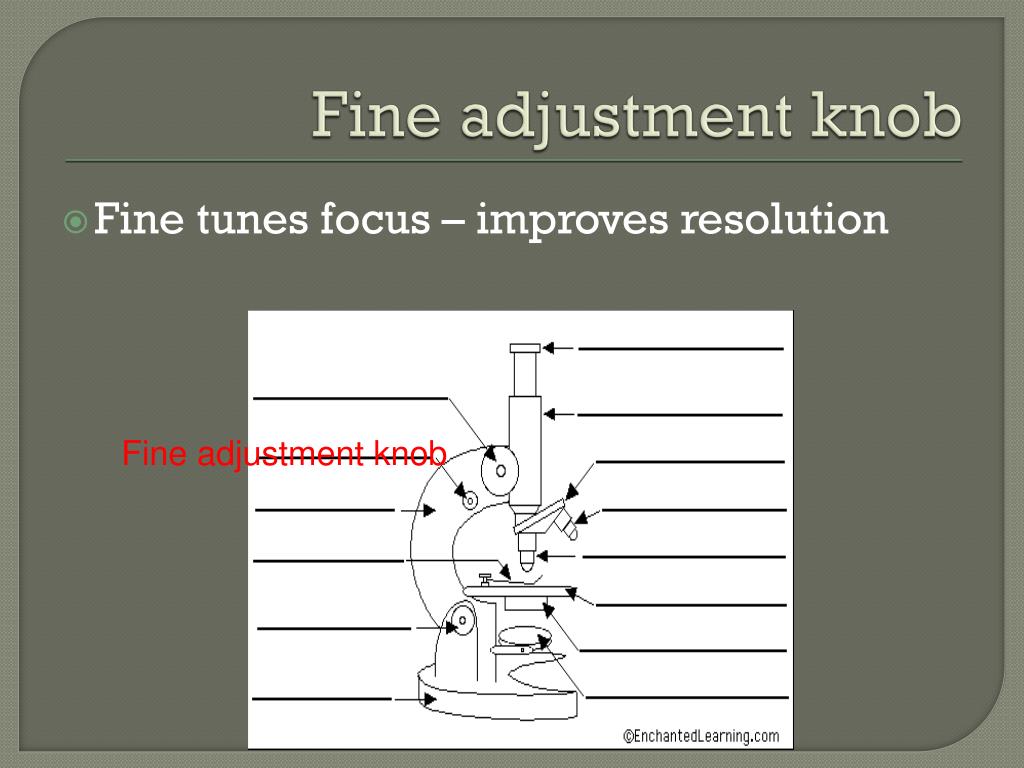
52010 Microscope Lab 2-1 THE MICROSCOPE Introduction: The microscope is a fundamental tool for biologists. This instrument has been perfected. FINE ADJUSTMENT KNOB — A slow but precise control used to fine focus the image when viewing at the higher magnifications. 6. BASE — The part of your microscope that sits on a level, stable support.

PPT The Microscope PowerPoint Presentation, free download ID819971
Stage adjustment knobs - located below the stage to control forward/reverse and side to side movement of the stage. Coarse adjustment knob - for focusing ONLY when using scanning objective lens. Fine adjustment knob -brings object into clearest focus. Iris diaphragm - controls the amount of illumination to improve contrast and resolution.

4 The Microscope Laboratory Manual For SCI103 Biology I at Roxbury Community College
Ocular Lens (eye-piece) Ocular lens of a microscope. It is located at the top of the microscope, and the ocular lens or eyepiece lens is used to look through the specimen. It also magnifies the image formed by the objective lens, usually ten times (10x) or 15 times (15x). Usually, a microscope has an eyepiece of 10x magnification power.

China Education Microscope, with Fine Adjustment Range (BM3A2) Photos & Pictures madein
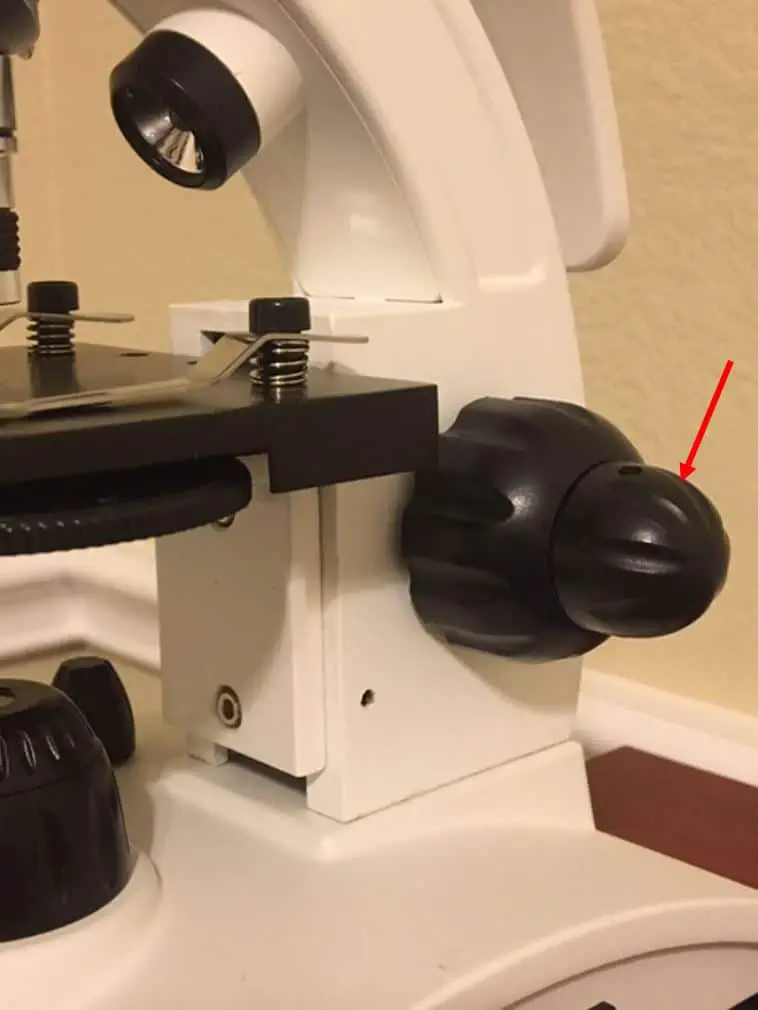
The fine adjustment knob is the smaller of the smaller of the two knobs and is located further away from the arm of the microscope. Most coarse and fine adjustment knobs are built with coaxial control in line with one another so you can easily switch from using the coarse focus adjustment knob to using the fine focus adjustment knob.
PPT Microscope Parts and Functions PowerPoint Presentation, free download ID1164888
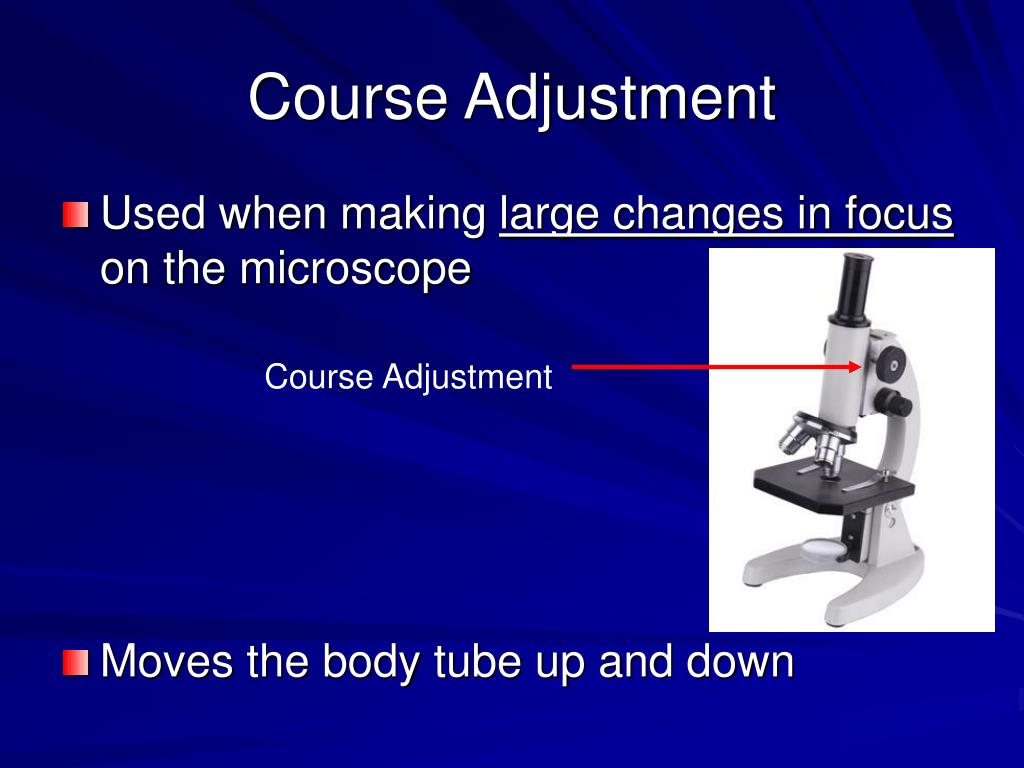
Coarse adjustment involves using the coarse adjustment knobs to rapidly raise or lower the microscope stage, bringing the specimen into a general focus. However, when dealing with stronger magnifications, a more delicate and controlled approach is required. This is where the fine adjustment knob comes into play.
Iris Diaphragm Lever Microscope Microscopy 1 This diaphragm is located closer to the light
Using coarse knob, focus using the 10x objective. Then adjust with FINE FOCUS knob on SMALLEST detail visible in the field. Now position 40x objective & adjust FINE FOCUS knob - you SHOULD NOT NEED TO TOUCH COARSE knob. Last EYE PIECES adjustment First - close LEFT EYE - then focus the image for your RIGHT EYE using fine focus knob.

40x 1000x Student Biological Microscope Fine Adjustment Knob Microscope A11.1010
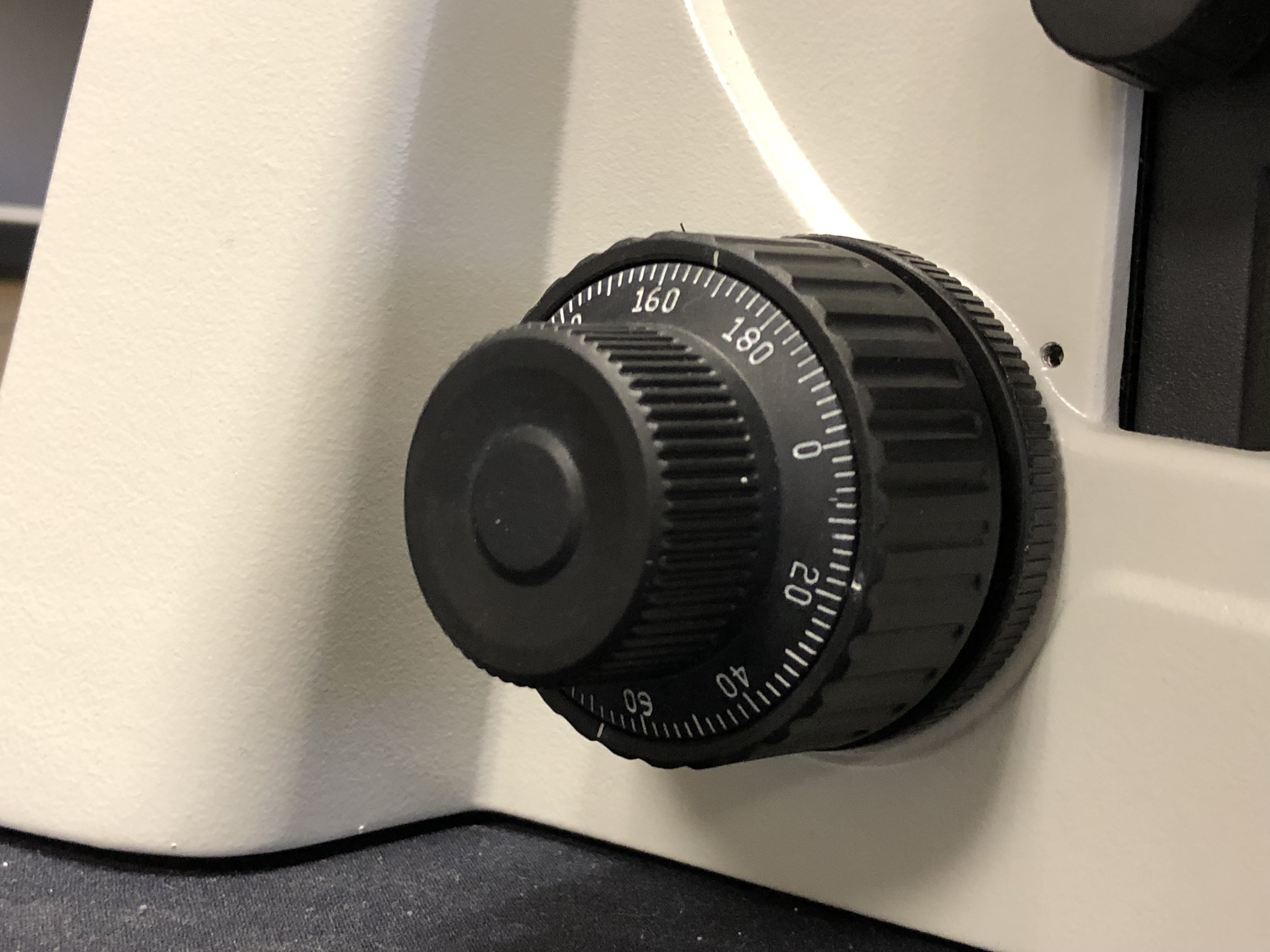
Fine adjustment knob Most types of microscopes have both knobs in different sizes to facilitate distinction between the two. The coarse adjustment knob brings the image into focus quickly, and the fine adjustment knob helps maintain the focus while you increase the magnification.

Microscope Coarse Adjustment and Fine Adjustment Explained Microscope Clarity
On some coaxial systems, the fine adjustment is calibrated, allowing differential measurements to be recorded. Comparison Microscope: A microscope that enables side-by-side viewing of two different specimens. The microscope has two sets of objectives with a single set of eyepieces (monocular or binocular), often used in forensic science.

Industrial Microscope Camera Fine Adjustment Bracket 360 Degree Free Rotation Adjustment Angle+
Coarse Focus Adjustment Knob; Fine Focus Adjustment Knob; Carefully plug in and position electric cord to avoid tripping or having the microscope pulled off the table. Turn on the microscope and rotate the nosepiece ring (turret) to snap the 10x objective lens in place. Do not use the objective lens to rotate!

Parts of a microscope
The Microscope Fine Adjustment. July 1916 Issue. The Sciences. This article was originally published with the title.

Parts of the Microscope (Labeled Diagrams) Simple and Compound Microscope
Fine focusing knob: smaller of the two knobs, the fine adjustment knob brings the specimen into sharp focus under low power and is used for all focusing when using high power lenses such as the 100x oil immersion lens. 6/9. Stage & Mechanical stage: The horizontal surface where you place the slide specimen is called the stage.

PPT Lab 1 PowerPoint Presentation, free download ID2063291
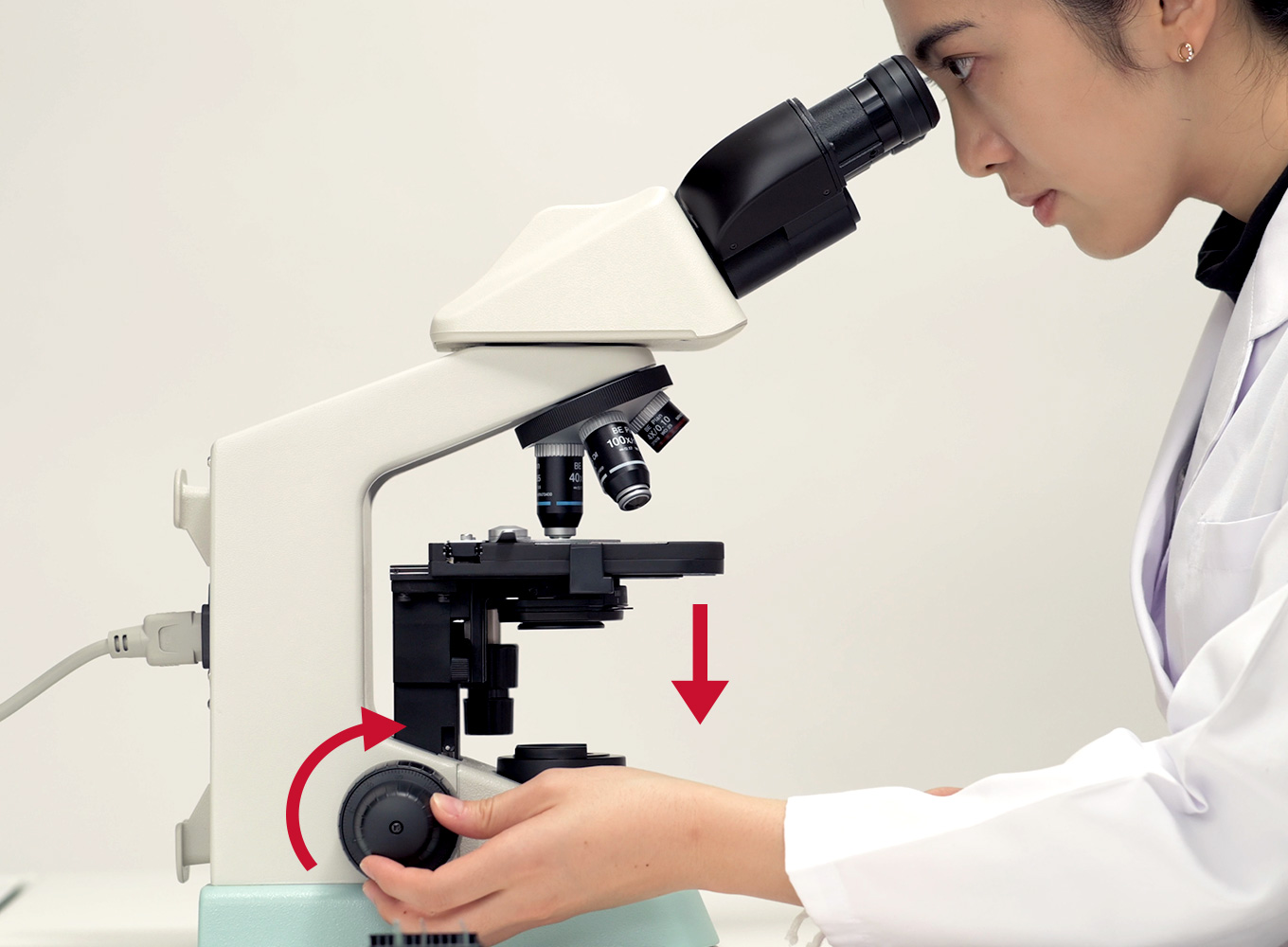
While looking through the ocular eyepiece, lower the stage SLOWLY using the coarse adjustment knob. Be sure that you are looking through the binocular head of the microscope with BOTH eyes. As soon as you see the specimen, STOP Using the coarse adjustment, and switch over to the fine adjustment knob.

3 Ways to Focus a Microscope Wiki How To English
Sharpen the focus, if necessary, with the coarse adjustment knob. Only a minimal amount of adjustment is usually necessary. Center the specimen in field, if necessary. Look at the microscope from the side: Rotate the high power objective into place very carefully! Look through the oculars: Using the fine adjustment knob only, sharpen focus.
Diopter adjustments(2)|Eclipse Guide|Nikon Corporation Healthcare Business Unit
Field Diaphragm Control - The base of the microscope contains the field diaphragm. This controls the size of the illuminated field. The field diaphragm control is located around the lens located in the base. Fine Adjustment Knob - This knob is inside the coarse adjustment knob and is used to bring the specimen into sharp focus under low power.

What are Coarse and Fine Adjustment on a Microscope? in 2020 Microscopic, Adjustable, Explained
The fine adjustment knob is an integral part of a microscope's focusing system. It is typically located on the microscope's frame and works in tandem with the coarse adjustment knob.

Diopter adjustments(2)|Eclipse Guide|Nikon Corporation Healthcare Business Unit
On both sides of the base of the microscope are the course and fine adjustment knobs, used to bring the image into focus. Rotation of these knobs will either move the specimen and the objectives closer or farther apart. The coarse adjustment moves the nosepiece in large increments and brings the specimen into approximate focus.